MALE ONCOFERTILITY: MAXIMIZING FERTILITY PRESERVATION THROUGH ADVANCED SPERM RETRIEVAL TECHNIQUES
When facing cancer treatments, preserving fertility becomes a critical concern for many men. Oncofertility bridges the gap between oncology and reproductive health, offering solutions to safeguard fertility despite the potential damage caused by cancer therapies. This blog focuses on sperm banking, testis biopsy, testicular sperm extraction, and microsurgical testicular sperm extraction (TESE and microTESE) as vital methods for fertility preservation.
The Importance of Sperm Banking for Fertility Preservation

Sperm banking, also known as sperm freezing, is a cornerstone of fertility preservation for men. It involves collecting and storing sperm before undergoing cancer treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation, or surgery. This process is essential for men wishing to preserve their fertility for future family planning.
Steps in Sperm Banking:
- Semen Collection: The individual provides a semen sample through masturbation. This sample is analyzed for sperm count, motility, and morphology.
- Sperm Freezing: The semen is mixed with a cryoprotectant and gradually cooled to protect sperm cells. It is then stored in liquid nitrogen at -196°C, ensuring long-term viability and preserving fertility.
Sperm banking is an ideal solution for men who can ejaculate, but alternative methods are available for those with challenges such as low sperm count or inability to ejaculate.
Advanced Sperm Retrieval Techniques
For men with azoospermia (no sperm in ejaculate) or who cannot ejaculate, advanced sperm retrieval techniques are crucial for fertility preservation:
Testicular Sperm Extraction (TESE)
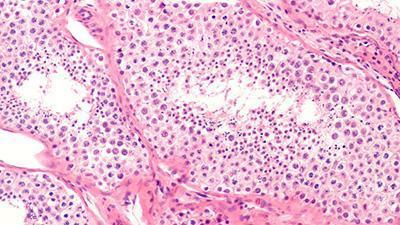
TESE is a surgical procedure that involves a testis biopsy to extract sperm directly from the testicular tissue. This method is especially beneficial for men with non-obstructive azoospermia, where sperm production is minimal.
- Procedure: A small incision is made in the scrotum under local or general anesthesia, and a piece of testicular tissue is removed. This tissue is processed to extract viable sperm.
- Benefits: TESE can retrieve sperm even in severely impaired sperm production cases, preserving fertility options.
Microsurgical Testicular Sperm Extraction (microTESE)
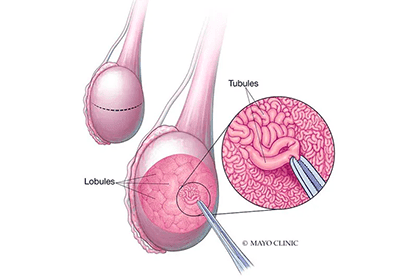
MicroTESE is a refined sperm retrieval technique that uses an operating microscope to identify sperm-rich seminiferous tubules.
- Procedure: Conducted under general anesthesia, microTESE involves smaller incisions and precise extraction of sperm-rich areas of the testis.
- Advantages: This technique improves sperm retrieval rates for men with non-obstructive azoospermia and minimizes testicular tissue damage, maximizing fertility preservation.
Epididymal and Vasal Sperm Retrieval
For men with obstructive azoospermia, where a blockage prevents sperm from reaching the ejaculate, these methods are used:
- Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration (PESA): A needle is inserted into the epididymis to aspirate fluid containing sperm.
- Microsurgical Epididymal Sperm Aspiration (MESA): A precise technique using a microscope to retrieve sperm from the epididymis.
- Vasal Aspiration: Sperm is retrieved directly from the vas deferens if a blockage is present downstream.
Choosing the Right Fertility Preservation Method
Selecting the appropriate sperm retrieval method depends on individual conditions, fertility goals, and available medical resources. Timing is crucial, and sperm retrieval should ideally occur before starting cancer treatments that might harm fertility.
Conclusion
Fertility preservation is vital for men undergoing cancer treatments. Sperm banking and advanced retrieval techniques like testicular sperm extraction and microsurgical testicular sperm extraction (TESE and microTESE) offer hope for preserving fertility despite the challenges of cancer therapy. As medical technology continues to advance, these options improve, providing better outcomes for patients and their families in their journey toward preserving fertility.

